Blockchain Privacy
On November 7, 2023
Introduction
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that enables secure, transparent, and decentralized storage and transfer of information. It uses cryptography and a consensus mechanism to ensure that transactions are validated and recorded accurately. The technology was first introduced as a component of Bitcoin, but has since been adapted and used in different industries and applications.
Blockchain privacy involves maintaining the confidentiality and safety of data stored on a blockchain. This can encompass personal information, financial dealings, and other confidential records stored on the blockchain. It is achieved through encryption, secure private keys, and other security procedures that deter unauthorized access and manipulation of the data.
Types of Blockchain
There are several forms of blockchain technology, each with its own specific features and attributes. The most common types include:
Public Blockchains: Also known as permissionless blockchains, public blockchains are accessible to anyone who wants to participate in the network. Anyone can join the network, validate transactions, and create new blocks. Public blockchains are typically considered the most secure due to their large network of nodes and advanced consensus mechanisms. Some examples of public blockchains are Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Private Blockchains: Also called permissioned blockchains, private blockchains are designed for specific organizations or groups. They are more centralized than public blockchains and require permission for participants to join the network. Private blockchains are often used by organizations that need to maintain control over the information stored on the network. Two examples of private blockchains are Hyperledger and Corda.
Consortium Blockchains: Consortium blockchains are similar to private blockchains, but are governed by a consortium of organizations rather than one entity. Consortium blockchains provide a balance between security, transparency, and decentralization, and offer a compromise between public and private blockchains. Examples of consortium blockchains include R3 and Energy Web Foundation.
Hybrid Blockchains: Hybrid blockchains are a combination of public and private blockchains, providing the benefits of both. They can be either permissioned or permissionless and allow organizations to tailor the technology to their specific needs. Hybrid blockchains are commonly used in industries such as finance and healthcare, where security and privacy are important.
In summary, blockchain technology is a versatile tool with the potential to revolutionize various industries and applications. The different types of blockchain technology provide organizations with the flexibility to choose the best solution for their needs, whether it be it public, private, consortium, or hybrid.
From below given statistics, we can see that worldwide spending on blockchain solution is increasing. This results in increase in users and applications of blockchain solutions resulting in the need to Thus, applications of blockchain solution are increasing and also the users, thus need to also increase the security and privacy to build safe environments. Formating
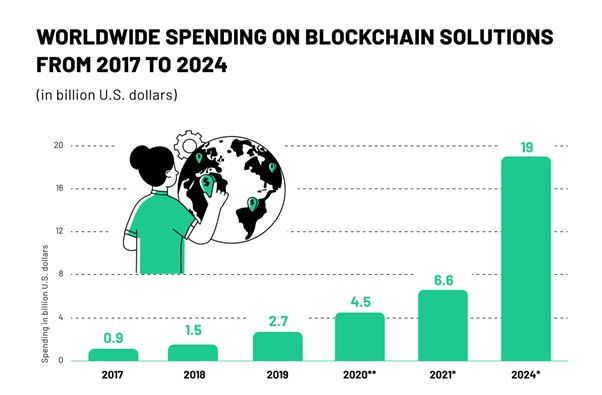 Figure 1: https://www.digitalinformationworld.com/2021/10/this-infographic-illustrates-10-biggest.html
Figure 1: https://www.digitalinformationworld.com/2021/10/this-infographic-illustrates-10-biggest.html
Security Measures
Blockchain technology has the potential to bring change to various sectors due to its decentralized and secure nature. Nevertheless, just like any other technology, it is not exempt from security risks and challenges. Enhancing the security of the blockchain system can be achieved by implementing the following measures:
Encryption: This involves converting plain text into a coded format, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users. Encrypting the data stored on the blockchain ensures the privacy and confidentiality of the data.
Cryptographic Hashing: This refers to the process of transforming data into a unique digital signature, also known as a hash, through a mathematical algorithm. Hashing assures the integrity of the data stored on the blockchain, as any alterations to the data would result in a different hash.
MultiSig Addresses: These are blockchain addresses that demand more than one signature to authorize a transaction, boosting the security of the blockchain system. This requires multiple parties to sign off on a transaction before it can be carried out.
Decentralization: This involves distributing data and processing power across multiple nodes, making it challenging for a single entity to control the network. Decentralizing the blockchain network guarantees stability and security of the system as there is no singular point of failure.
Frequent Audits and Upgrades: Regular audits and upgrades are essential in identifying and fixing security vulnerabilities in the blockchain system. This helps to maintain the system’s security and resistance to attacks.
Two-Factor Authentication: This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of authentication before accessing the blockchain system, such as sending a password and an OTP to a user’s mobile device.
Safe Private Keys: Private keys are utilized to access and authorize transactions on the blockchain. Ensuring the safety of private keys is vital for the security of the blockchain system, as a breached private key can result in the loss of assets stored on the blockchain.
Threats & Mitigations
Some of the common threat issues in blockchain technology and the mitigation techniques include:
51% Attack: A 51% attack occurs when a group of nodes controlling more than 50% of the network’s computing power manipulate the network’s consensus mechanism.
Mitigation: To reduce this threat, blockchain networks should have a decentralized network structure that makes it difficult for a single entity to control a majority of the network’s computing power.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts are automated programs that run on the blockchain, but vulnerabilities in the code of smart contracts can be exploited by attackers to steal assets or disrupt the network.
Mitigation: To tackle this threat, blockchain developers must ensure that their smart contracts undergo thorough security audits and testing.
Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks are a type of social engineering attack that aims to obtain sensitive information such as login credentials or private keys.
Mitigation: To counteract this threat, blockchain users should be educated on how to identify phishing attempts and avoid giving out their personal information or private keys.
Data Tampering: Data tampering is the unauthorized modification of data stored on the blockchain.
Mitigation: To address this threat, blockchain networks can use cryptographic algorithms such as hash functions to preserve the integrity of the data stored on the blockchain.
Network DDoS Attacks: A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is an attack where a large number of nodes simultaneously send requests to a network, causing it to become overwhelmed and unavailable to other users.
Mitigation: To mitigate this threat, blockchain networks can implement anti-DDoS measures such as rate limiting, IP blocking, and traffic filtering.
Conclusion
Despite being a secure technology, blockchain is still susceptible to security threats and challenges. To ensure the stability and security of the blockchain system, it is necessary to understand the various types of threats and their respective mitigation techniques. This can be achieved through education, the implementation of security measures, and the use of secure network structures.
1. How Blockchain Technology Can Help Enhance Your Cybersecurity?
Blockchain technology has the potential to significantly improve cybersecurity and reduce the risk of cybercrime. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain makes it difficult for hackers to attack and manipulate the data stored on the platform, which enhances the security of online transactions. Here are some of the key ways that blockchain can help enhance cybersecurity.
Immutable Ledgers
The ledger of transactions on a blockchain is immutable, meaning once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes it difficult for hackers to tamper with the data, reducing the risk of fraud and other forms of cybercrime. The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that data is secure and trustworthy, which is particularly important for sensitive information such as financial transactions and personal data.
Decentralized Network
One of the biggest advantages of blockchain technology is its decentralized architecture. Unlike traditional systems, which are centralized and have a single point of control, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, making it more difficult for hackers to carry out successful attacks. In the event that one node in the network is compromised, the rest of the network can continue to operate normally, reducing the risk of widespread disruption.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that automatically enforce the terms of an agreement between parties. By eliminating the need for a third party to oversee transactions, smart contracts reduce the risk of fraudulent activity and enhance cybersecurity. Smart contracts provide a secure and transparent way to execute transactions, ensuring that the terms of the agreement are met and reducing the risk of fraud and other forms of cybercrime.
Secure Identity Management
Blockchain technology can be used to securely manage digital identities, making it difficult for criminals to steal and misuse them. By storing identity information on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible for hackers to access or manipulate it. This enhances the security of digital identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and other forms of cybercrime.
Supply Chain Security
Blockchain can also be used to secure supply chains by providing an immutable record of the origin and movement of goods. This can help prevent counterfeiting and other types of fraud, as well as improve transparency and accountability in the supply chain. By tracking the movement of goods from origin to destination, blockchain provides a secure and transparent way to manage supply chains, reducing the risk of cybercrime and enhancing the overall security of the supply chain.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers significant benefits for enhancing cybersecurity and reducing the risk of cybercrime. With its decentralized architecture, immutable ledgers, secure identity management, smart contracts, and supply chain security, blockchain provides a powerful tool for organizations to secure their online transactions and protect against cybercrime. By leveraging these benefits, organizations can reduce the risk of cybercrime and improve the security of their online transactions, protecting their sensitive information and assets.
2. Exploring the Interplay Between Blockchain and Cybersecurity
The combination of blockchain technology and cybersecurity can lead to a significant improvement in the security of digital transactions and data storage. We will look, how both blockchain and cybersecurity can help each other: -
Improving Cyber Security through Blockchain
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized platform for data storage and transactions, which makes it more secure and resistant to cyber-attacks compared to traditional centralized systems.
The absence of a single controlling entity (centralized) eliminates the risk of a single point of failure, reducing the likelihood of a successful cyber-attack.
It can be improved by adopting other fields such as: -
Increased Trust through Smart Contracts: The use of smart contracts in blockchain technology can help improve cybersecurity by reducing the risk of fraud and tampering. Transactions are automatically executed based on pre-defined rules, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing the trust in digital transactions.
Tamper-Proof Record Keeping: Blockchain technology provides an immutable, or unalterable, record of all transactions. This tamper-proof record keeping can help improve cybersecurity by providing a secure and transparent record of digital transactions, making it easier to detect and prevent fraudulent activity.
Increased Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent and traceable record of transactions, which can help improve cybersecurity by making it easier to detect and prevent fraudulent activity. The transparency of blockchain transactions makes it easier for organizations to track the flow of digital assets and detect any anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
Improving Blockchain through Cybersecurity Measures
Cybersecurity can play a critical role in improving the security of blockchain technology.
Cybersecurity experts can identify potential vulnerabilities in blockchain systems and implement security measures such as: -
Encryption: The use of encryption is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyber-attacks. Advanced encryption algorithms, such as AES and RSA, can be used to secure blockchain transactions and protect sensitive information.
Secure Key Management: The secure management of private keys is essential to ensure the security of blockchain transactions. The safe storage of private keys, either through hardware wallets or other secure solutions, is critical to prevent theft or loss.
Multi-Factor Authentication: By adding an extra layer of security, multi-factor authentication can improve the safety of blockchain transactions. This can include the use of biometrics, passwords, and smart cards to confirm the identity of users before accessing sensitive information.
Software Updates and Patches: Regular software updates and patches are important to keep blockchain systems secure and prevent potential vulnerabilities. By staying up-to-date with the latest security updates, organizations can ensure the continued stability and security of their blockchain systems.
Conclusion
By working together, blockchain and cybersecurity can enhance trust in digital transactions, reduce the risk of fraud, and improve the overall security of the digital world.
3. Exploring the Role of Blockchain in Cybercrime Prevention
The application of blockchain technology in the field of cybercrime prevention has several benefits and can play a crucial role in improving the overall security of the digital world. The following are some of the ways blockchain can be utilized to prevent cybercrime:
Digital/Evidence Identity Management
Digital/Evidence Identity Management with blockchain is a system that manages digital identities and their associated evidence using blockchain technology. This system securely stores and manages digital identities on a decentralized blockchain network that is resistant to tampering. By storing digital identities on a decentralized blockchain, personal information can be protected from cybercriminals who might attempt to steal or manipulate this information. This provides a secure and efficient way to manage digital identities.
Traffic Violation Monitoring System
A Traffic Violation Monitoring System in blockchain is a system that uses blockchain technology to keep track of traffic infractions such as speeding, running red lights, or reckless driving. The information regarding these violations is securely stored on a decentralized, tamper-proof blockchain network that can be accessed and verified by authorized entities like law enforcement, insurance companies, and government organizations. By utilizing blockchain, this system offers a transparent, accurate, and secure way of recording and monitoring traffic violations, improving road safety and reducing the number of accidents on the road.
Malware Prevention
Malware Prevention in blockchain involves using blockchain technology to stop the transmission and harm caused by malware in digital systems. In this system, the data and software related to the blockchain network are securely kept and managed on a decentralized, tamper-resistant blockchain network, making it harder for malware to penetrate and harm the system. The use of consensus methods and cryptographic techniques in blockchain also offers a secure and dependable method for verifying software, making it easier to identify and prevent malware attacks. Thus, making it more challenging for cybercriminals to access sensitive information or carry out malware attacks.
Cybersecurity Information Sharing
Blockchain can help organizations and government agencies to share information about cybersecurity threats in real-time. This allows for a more effective and timely response to potential cyber threats.
Secure and Transparent Transactions
The decentralized ledger of blockchain ensures that transactions are recorded in a transparent and secure manner, making it difficult for cybercriminals to manipulate transactions and steal sensitive information.
Fraud Prevention
Blockchain can help prevent fraud in various industries such as banking, e-commerce, and supply chain management by providing a secure and transparent record of transactions. It can also make it simpler to monitor and follow fraudulent activities due to its transparency and unalterable nature, giving a lasting and verifiable record of all transactions. By offering a secure and open platform for transactions, blockchain has the ability to greatly enhance the security and efficiency of various industries and stop fraudulent activities.
DDoS Protection
By creating decentralized networks, blockchain can make it more difficult for cybercriminals to carry out DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks, which aim to disrupt the availability of online services.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain and cybersecurity can help organizations take a proactive approach to enhancing their cybersecurity and protect against potential cyber-attacks. By implementing blockchain solutions, businesses can secure digital assets, protect against cyber threats, and build trust in the digital world. As the demand for secure online transactions continues to grow, the use of blockchain in the field of cybercrime prevention is becoming increasingly important.
4. Exploring the Potential of Blockchain for Improved Cybersecurity
The integration of blockchain technology with cybersecurity has the potential to greatly improve the security of the digital world in the future. Here are some of the most promising use cases for blockchain in cybersecurity:
Safe Identity Management
Blockchain has the potential to create secure, decentralized digital identities which can reduce the chances of identity theft and fraud. This can guarantee that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information and systems, increasing overall cybersecurity.
Decentralized Data Storage
By using blockchain, data can be securely stored on a decentralized ledger, making it much less vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. This will ensure sensitive information stays secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Improved Cyber Threat Intelligence
Blockchain can be used to store and share real-time information about cyber threats, allowing organizations to respond to potential threats more quickly and effectively. By keeping a secure and transparent record of all transactions, blockchain can help organizations prevent and identify potential cyberattacks.
Secure Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can be used to secure and track the supply chain, making sure that sensitive information stays protected. This will reduce the risk of cyberattacks and improve overall cybersecurity.
Improved Incident Response
Blockchain can be utilized to store and share real-time information about cybersecurity incidents, allowing organizations to respond to potential threats quickly and effectively.
Secure Networks
One potential application of blockchain for improved cybersecurity is in the creation of secure networks. This can be especially useful for protecting sensitive information such as personal and financial data, as well as intellectual property. By using blockchain technology, organizations can create secure networks that are resistant to hacking and tampering, ensuring the protection of sensitive information.
Smart Contracts
Another potential use of blockchain is the creation of smart contracts. These self-executing contracts can be programmed with specific terms and conditions, which are automatically executed once certain conditions are met. This can greatly improve cybersecurity by reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that contracts are executed exactly as intended.
Log Management
The logs can be generated by various systems, applications, and devices, and are stored on a blockchain network. The network provides a secure and decentralized platform for storing and accessing the logs, making it difficult for malicious actors to tamper with or manipulate the logs. This makes log management through blockchain a useful tool for auditing, compliance, and cybersecurity purposes.
IOT
Blockchain technology can also be used to improve the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. By creating secure networks of IoT devices using blockchain technology, organizations can protect against cyberattacks and ensure the security of connected devices. This can have far-reaching implications for industries such as healthcare, where connected devices play a crucial role in the delivery of care.
Conclusion
The potential of blockchain technology for improved cybersecurity is vast. From creating Safe Identity Management to improving the security of IoT devices, to revolutionizing identity and access management, the possibilities are nearly endless. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more innovative uses for blockchain in the realm of cybersecurity.
What the Latest Research Says About Blockchain Privacy and Cybersecurity
Blockchain technology has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its secure, transparent, and decentralized nature. It has the potential to revolutionize various industries, but at the same time, it is not immune to security threats and challenges. This has led to a growing interest in the latest research on blockchain privacy and cybersecurity.
Studies have shown that public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are susceptible to various privacy attacks, such as linkability and deanonymization. These attacks can compromise the confidentiality and privacy of users, making it important for public blockchains to implement privacy-preserving techniques.
One such technique is the use of zero-knowledge proofs, which allow transactions to be verified without revealing any sensitive information. Another is the use of privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, such as Monero and ZCash, which use advanced encryption methods to enhance the privacy of transactions.
In terms of cybersecurity, research has focused on the potential vulnerabilities of blockchain systems and how to improve their security. For instance, studies have shown that smart contracts, self-executing code used in blockchain applications, can contain vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. This highlights the importance of regularly auditing and updating smart contracts to ensure their security.
In addition, research has also shown that the use of decentralized applications (dApps) built on blockchain platforms can also be vulnerable to security threats, such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection attacks. To mitigate these risks, researchers have proposed the use of secure coding practices and the implementation of security standards for dApps.
Another area of focus in blockchain security research is the protection of private keys, which are critical for accessing and authorizing transactions on the blockchain. Research has shown that poor key management practices, such as storing keys on unsecured devices, can lead to the theft of assets stored on the blockchain. To address this issue, researchers have recommended the use of secure hardware wallets, multisig addresses, and two-factor authentication (2FA) to protect private keys.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology holds enormous potential for various industries, but at the same time, it is not immune to privacy and security risks. The latest research in the field of blockchain privacy and cybersecurity provides valuable insights into the potential vulnerabilities of blockchain systems and how to improve their security. By adopting these findings, organizations can ensure the security and privacy of their blockchain systems and maximize the potential benefits of this revolutionary technology.





