RedOps (Red Team Operations)
On November 18, 2023
What is RedOps?
RedOps stands for Red Team Operations, where Security Professionals (Red Team Operators) simulate real-world attacks on a company’s systems, processes, and people. The reason for having this engagement is that it is better that a known attacker finds the open vulnerability rather than a bad actor. The purpose of the engagement is to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s security posture that could be exploited by real attackers.
In Red Team Engagements the Security Professionals where the Red Team Operators will try everything to get access to the crown jewels. It is an all-in approach where there are no planned attacks or any exceptions in place although there are some companies have which mostly put exceptions on things like DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attacks. During Red Ops there is a cycle which is followed which starts from Recon/OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence) and ends with Data Exfiltration.
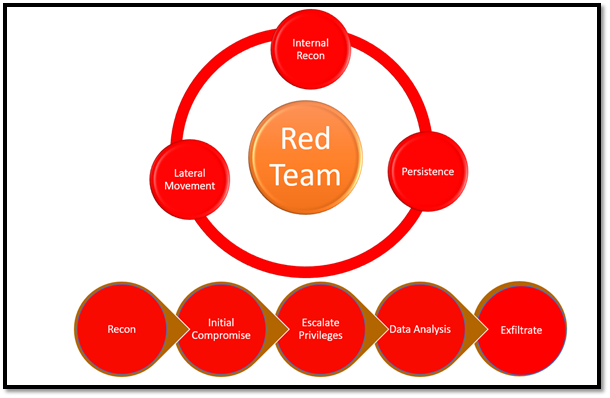
Each Stage of Red Team Engagement is different from one another
1. Recon- In First Phase of Recon is done where all the information assets is gathered including (Domains, Subdomains, IPs, Emails, Leaked Credentials, etc.). Vulnerability Identification over Web Applications is also done and external IPs assessed for any known vulnerability through which initial compromise could be done.
2. Initial Compromise- In second phase the Initial Compromise is done and foothold is established into the organization, vulnerabilities identified in the first phase are exploited in here. If no vulnerability is identified then Red Team Operators might use other attack vectors including Physical Security, Social Engineering (Phishing, Vishing, etc.) and gain access into the network.
3. Privilege Escalation- In third phase the access one has is escalated to the root/Admin Privileges here Red Team Operators may use an existing vulnerability or develop exploits where they can bypass the Security Restrictions of the machine-like Anti-Virus, EDR, etc.
4. Persistence- In Fourth Phase, persistence is done so even if SOC/Security Team removes the payload another backdoor is present through which Red Team Operators can regain the access which might have been removed. Often at this stage C2 (Command and Control) Agents are installed through which they can remotely access and send commands to the victim machine.
5. Internal Recon- In Fifth Phase the recon is done of the internal network where the internal network is assessed for assets and servers and vulnerabilities upon them can be exploited.
6. Lateral Movement- At sixth phase of Red Team Engagement Lateral Movement is done through which the Red Team Operators avoid being detected and are able to Pivot to other machines as and when required and essentially gain complete control over the network.
7. Data Analysis- At this Phase the Data which has been gathered through Exploitation is Analysed and is divided between useful and useless data.
8. Data Exfiltration- This is usually the last phase where Data from compromised endpoints is exfiltrated to the C2 Server and then later shown as POC to the clients.
The above mentioned was a small summary of the activities included in Red Team Engagement, but it goes way beyond the above-mentioned phases there are times where in Physical Attacks the Red Team Operators needs to do stuff like RFID Hacking, NFC Hacking, various types of Social Engineering and also doing Physical Security checks.
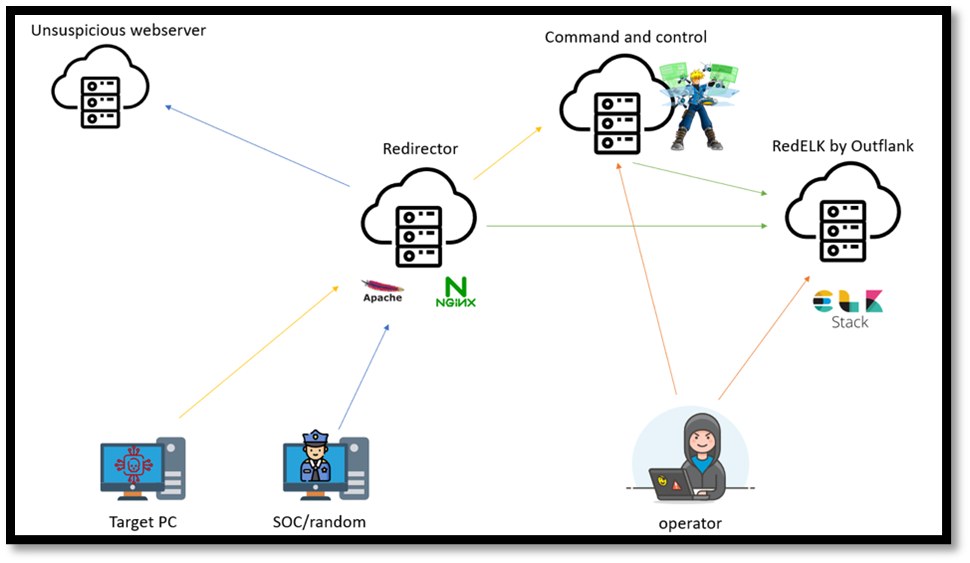
Typical Red Team Infrastructure:
A Typical Red Team Infrastructure consist of following: • Multiple C2 Servers
• Redirectors
• Phishing Sites
• Reverse Proxys
• RedELK (Optional, but a great value Add)
Benefits of Red Team Engagement:
• Identifying Weakness: Red Team Engagements can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s security defenses that may have been overlooked or not detected by other security testing methods by simulating real-world attack scenarios, the red team can provide insights into the effectiveness of the organization’s security controls and identify areas for improvement.
• Testing Incident Response- Red Team Engagements can also help test an organization’s ability to detect and respond to security incident by attempting to penetrate the organization’s defenses, the red team can test the effectiveness of the organization’s incident response plan and identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
• Improving security awareness: Red Team Engagements can help raise awareness among employees about the importance of security and the need to follow security policies and procedures by using social engineering and other tactics to target employees, the red team can identify areas where additional training and awareness-building efforts may be needed.
Monitoring the Blue Team Activities
There are several benefits for Red Team to monitor the Blue Team’s activity, some of them are:
• Measuring SOC Team’s Effectiveness: By this SOC Team’s response time and the activities conducted for detection and response can be tracked. Additionally, any gaps in the Process and Procedure can also be identified. This will also give insight to SOC Team on where there defences can be strengthened.
• Enhancing Situational Awareness: Because of this kind of Scenarios the SOC Team will be able to focus on the areas where they weren’t focusing before and the same will help them build more use cases and make the overall SOC more effective
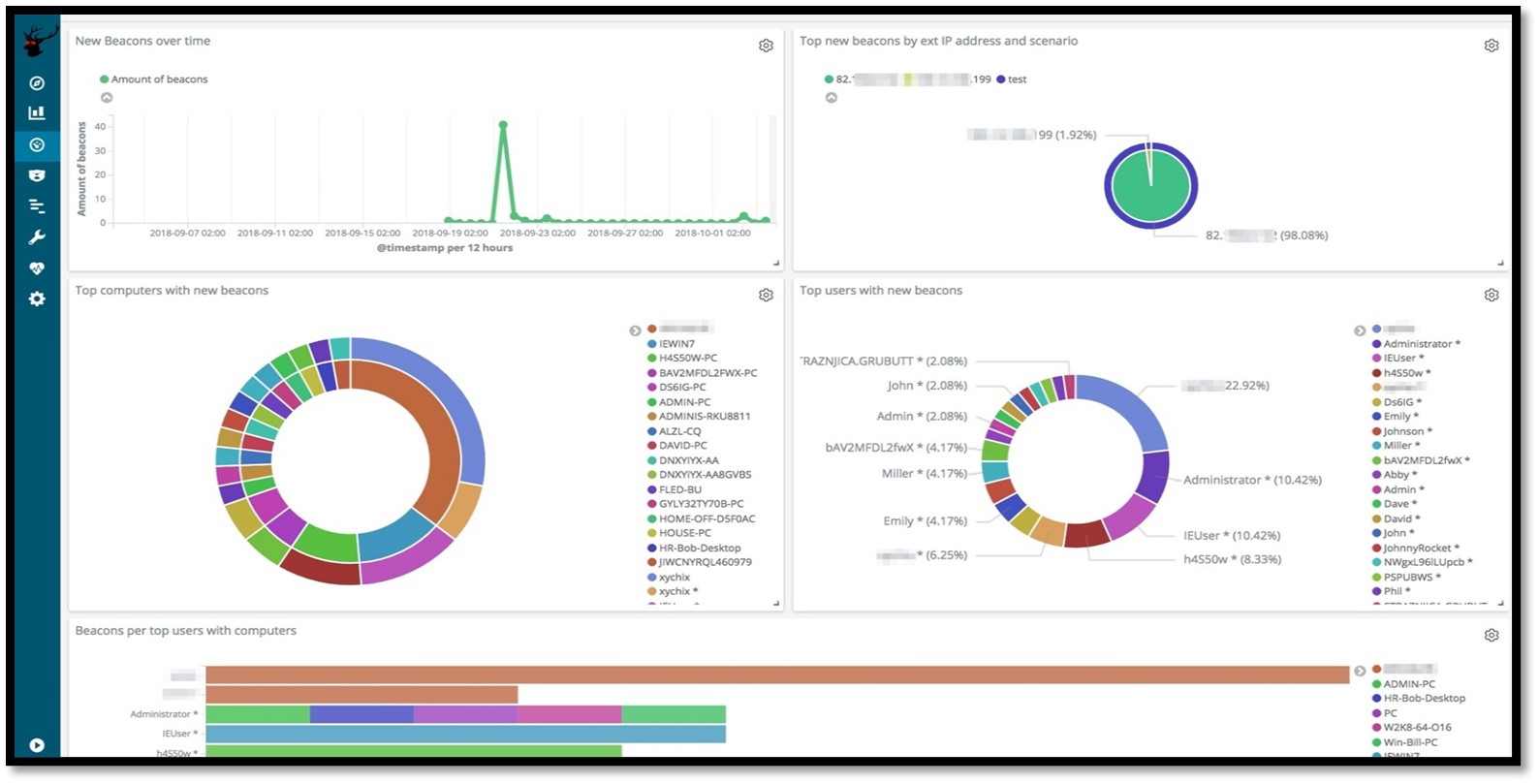
RedELK is one of the SIEM we use incorporating our C2 Agents logs and the endpoint logs. RedELK also has features of Threat Intel built in which can also track if one of our C2 Payloads gets detected by an AV we will get a notification for it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, red teaming is an essential element of a robust security program. By simulating real-world attacks, red teams can identify weaknesses in an organization’s security infrastructure and help to improve overall security posture.





